A dual-channel chemodosimetric sensor for discrimination between hypochlorite and nerve-agent mimic DCP: application on human breast cancer cells†
Abstract
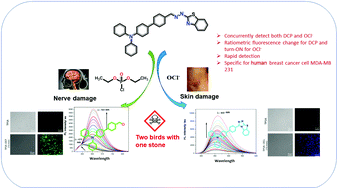
A styryl bridge containing a triphenylamine–thioimidazole hydrazine-based dual-analyte-responsive fluorescent sensor was designed and synthesized for the detection of the nerve gas simulant diethyl chlorophosphate (DCP) and hypochlorite (OCl−) for the first time. Hypochlorite induces oxidative intramolecular cyclization to give a triazole structure, which exhibited blue fluorescence with excellent selectivity and a low detection limit (8.05 × 10−7 M) in solution. Conversely, the probe forms a phosphorylated intermediate with diethyl chlorophosphate, which undergoes further hydrolyzation and presents green fluorescence in a ratiometric mode with a low detection limit (3.56 × 10−8 M). Additionally, the as-designed sensor was utilized to construct a portable kit for real-time monitoring of DCP in a discriminatory, simple and safe manner. Lastly, the probe was also productively employed for in situ imaging of OCl− and DCP in the living cell.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...