The copper-catalyzed oxidation of arylmethyl triazines with H2O toward the oxidant-free synthesis of aroyl triazines†
Abstract
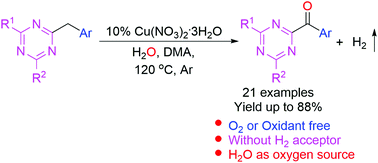
We report an efficient copper-catalyzed dehydrogenation method for the synthesis of aroyl triazines from arylmethyl triazines with water in the absence of additional oxidants or hydrogen acceptors. The use of substrates with both electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups resulted in moderate to good yields. Using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, 18O-labeled-water reactions and hydrogen capture experiments confirmed that water was the only oxygen donor and hydrogen was the by-product. This oxidation strategy provides a new approach for the synthesis of aroyl triazines with a broad substrate scope.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...