Electrochemical thiocyanation of barbituric acids†
Abstract
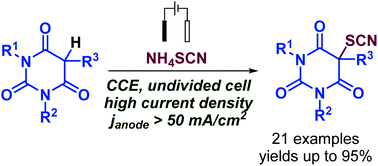
The electrochemical thiocyanation of barbituric acids with NH4SCN was disclosed in an undivided cell under constant current conditions. The electrosynthesis is the most efficient at a record high current density (janode ≈50–70 mA cm−2). NH4SCN has a dual role as the source of the SCN group and as the electrolyte. Electrochemical thiocyanation of barbituric acids starts with the generation of (SCN)2 from the thiocyanate anion. The addition of thiocyanogen to the double bond of the enol tautomer of barbituric acid gives thiocyanated barbituric acid. A variety of thiocyanated barbituric acids bearing different functional groups were obtained in 18–95% yields and were shown to exhibit promising antifungal activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...