Supramolecular self-associating amphiphiles: determination of molecular self-association properties and calculation of critical micelle concentration using a high-throughput, optical density based methodology†
Abstract
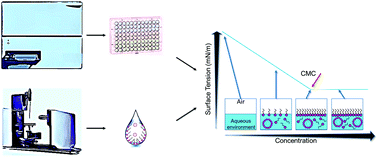
Supramolecular self-associating amphiphiles are a class of amphiphilic salt, the anionic component of which is ‘frustrated’ in nature, meaning multiple hydrogen bonding modes can be accessed simultaneously. Here we derive critical micelle concentration values for four supramolecular self-associating amphiphiles using the standard pendant drop approach and present a new high-throughput, optical density measurement based methodology, to enable the estimation of critical micelle concentrations over multiple temperatures. In addition, we characterise the low-level hydrogen bonded self-association events in the solid state, through single crystal X-ray diffraction, and in polar organic DMSO-d6 solutions using a combination of 1H NMR techniques. Moving into aqueous ethanol solutions (EtOH/H2O or EtOH/D2O (1 : 19 v/v)), we also show these amphiphilic compounds to form higher-order self-associated species through a combination of 1H NMR, dynamic light scattering and zeta potential studies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...