Development of a synthetic equivalent of α,α-dicationic acetic acid leading to unnatural amino acid derivatives via tetrafunctionalized methanes†
Abstract
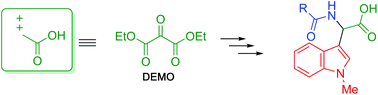
Diethyl mesoxalate (DEMO) exhibits high electrophilicity and accepts the nucleophilic addition of a less nucleophilic acid amide to afford N,O-hemiacetal. However, our research showed that elimination of the amide moiety proceeded more easily than dehydration upon treatment with a base. This problem was overcome by reacting DEMO with an acid amide in the presence of acetic anhydride to efficiently obtain N,O-acetal. Acetic acid was eliminated leading to the formation of N-acylimine in situ upon treatment with the base. N-Acylimine is also electrophilic, accepting the second nucleophilic addition by pyrrole or indole to form α,α-disubstituted malonates. Subsequent hydrolysis followed by decarboxylation resulted in (α-indolyl-α-acylamino)acetic acid formation; homologs of tryptophan. Through this process, DEMO serves as a synthetic equivalent of α,α-dicationic acetic acid to facilitate nucleophilic introduction of the two substituents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...