A core/shell nanogenerator achieving pH-responsive nitric oxide release for treatment of infected diabetic wounds†
Abstract
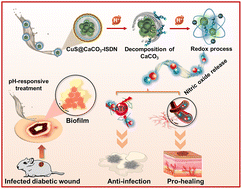
Nitric oxide is critical for eliminating infection and promoting regeneration in diabetic wounds. However, clinical uses of nitric oxide are limited by its high activity and lack of specificity in targeting infections. Herein, we develop an intelligent nitric oxide nanogenerator comprising isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN)-coated copper sulfide (CuS)/calcium carbonate (CaCO3) core/shell nanoparticles (CuS@CaCO3-ISDN) to target the acidic microenvironment of the infected diabetic wounds. Meaningfully, triggered by acid decomposition of CaCO3, this nanogenerator can achieve a responsive and accelerated release of nitric oxide from ISDN through enzyme-mimicking redox processes that involve CuS nanoparticles and then inactivate biofilm bacteria through the pathways of oxidative stress and disruption of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-related energy metabolism. Moreover, after eliminating the infection, the pH-responsive release of nitric oxide can promote the proliferation of blood vessels and tissue regeneration and accelerate diabetic wound closure. This study expands the use of nitric oxide donors in wound treatment by developing the enzyme-mimicking release strategy, and the pH-responsive core/shell nanogenerator is promising for a variety of anti-infection therapeutic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...