Microwave-assisted NixFe1−x nanoclusters ultra-stable to oxidation in aqueous media†
Abstract
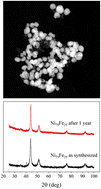
Metal alloy nanoparticles, and, in particular, permalloy, still hold an untapped potential in nanotechnology, although their poor stability against oxidation due to environmental exposure limits their use in many technological applications, and even more in life sciences. We propose a scalable single-step microwave-assisted method to produce water suspensions of Ni1–xFex nanoparticles without the need for an inert atmosphere, either organic solvents or any type of post-processing. We use hydrazine as a reducer, iron(II), iron(III) and nickel(II) chloride as precursors, 1,12-dodecanediol as a surfactant and water as a reaction medium. The mixture is heated at 160 °C for 10 minutes to obtain uniform alloy nanoparticles with sizes of around 24.5 nm for Ni (0% Fe) and 5.5 nm for 35% Fe that are forming uniform aggregates with sizes between 200 nm for Ni and 65 nm for iron oxide NPs. A linear increase of saturation magnetization is observed with an Fe content of up to 25%, whereas for larger percentages a sudden drop takes place due to the formation of iron oxides. X-ray diffraction measurements rule out the formation of any oxides after more than one year of storage at 4 °C, surely due to the presence of 1,12-dodecanediol at the surface, as evidenced by infrared spectroscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...