Conjugating AIE-featured AuAg nanoclusters with highly luminescent carbon dots for improved visible-light-driven antibacterial activity†
Abstract
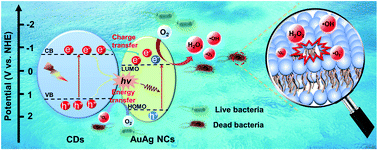
Metal nanoclusters (NCs) have emerged as novel antibacterial agents featuring broad-spectrum antibacterial activity without drug resistance for bacteria, but suffer from fast antibacterial invalidation due to their consumption by bacteria. Herein we report the design of a visible-light-driven photodynamic antibacterial agent based on conjugating aggregation-induced emission (AIE)-featured AuAg NCs with highly luminescent carbon dots (CDs). The conjugation of CDs with AuAg NCs could not only enhance the visible-light harvest, but also promote charge carrier generation/separation via charge/energy transfer, leading to the production of abundant reactive oxygen species (ROS) for bacterial killing under visible-light irradiation. Consequently, the as-obtained CDs@AuAg NCs display excellent photodynamic antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria with 4–5 orders of magnitude reduction in colony forming units, which is different from the conventional metal NC-based analogue relying on self-consumption for bacterial killing. In addition, the CDs@AuAg NCs are found to be free of cytotoxicity; the ROS capture experiments indicate that the photoproduced H2O2 by CDs@AuAg NCs is the main active species for bacterial killing, accounting for nearly 48% of the total antibacterial efficacy. This study provides a paradigm for the design of metal NC-based photodynamic antibacterial agents for diverse bactericidal applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...