N-gene-complementary antisense-oligonucleotide directed molecular aggregation of dual-colour carbon dots, leading to efficient fluorometric sensing of SARS-COV-2 RNA†
Abstract
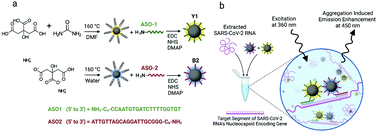
The early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic punctuated the need for rapid, mass testing for early detection of viral infection. Carbon dots are easily synthesized, cost-effective fluorescent nanoparticles whose surface functionalities enable facile conjugation with biorecognition elements suitable for molecular detection of viral RNA. Herein, we report that a pair of complementary antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) sequences can lead to a highly specific molecular aggregation of dual colour carbon dots (CDs) in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. The nanoprobes used ASOs highly specific to the N-gene of SARS-COV-2. When the ASOs are conjugated to blue and yellow citric acid-derived CDs, the combination of the ASO-CD pairs facilitates aggregation-induced emission enhancement (AIEE) of the measured fluorescence after hybridization with SARS-CoV-2 RNA. We found the sensor capable of differentiating between MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 samples and was found to have a limit of detection of 81 copies per μL. Additionally, we used dialysis to demonstrate that the change in emission upon aggregation is dependent on the compositional heterogeneity of the conjugated-carbon dot mixture.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...