Preparation and properties of multifunctional phenoxyacetate-based ionic liquids and their application in citrus bacteriostatic preservation†
Abstract
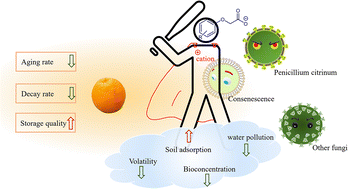
Recently, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid, and 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid have been extensively used as herbicides in field crops and they can also act as a plant growth regulator at low concentrations. However, these compounds possess high vapor pressure and high volatility. In this regard, the introduction of ionic liquids (ILs) has emerged as an effective approach to overcome these shortcomings. The present study aimed to prepare a series of ILs with bactericidal activity cations and phenoxyacetic acid series compounds as anions. The synthesized compounds were tested for their physicochemical properties, antibacterial activity and citrus preservation through experiments. ILs showed lower volatility, better soil adsorption capacity, and dual functions of plant growth regulation and antibacterial activity. The tested ILs effectively delayed the aging rate of citrus, reduced the decay rate, inhibited citrus storage diseases, and improved the storage quality of citrus. Overall, the study results provide a theoretical basis for the development of sustainable multifunctional ILs by introducing anions and cations with targeted effects. These newly synthesized ILs allowed us to achieve benefits far exceeding the simple additive rule, improving the physical and chemical properties and reducing environmental pollution by decreasing the amount of chemicals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...