Design and synthesis of 1,3-diphenylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione derivatives as antitumor agents via elevating ROS production to induce apoptosis†
Abstract
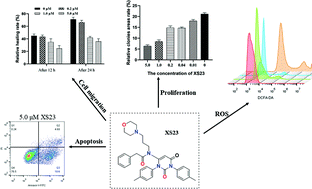
Elevating cancer cell intracellular ROS production has been proven to be effective for cancer therapies. In this work, a series of 1,3-diphenylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione derivatives were designed and synthesized, of which the target compound XS23, N-(2,6-dioxo-1,3-di-m-tolyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-4-yl)-N-(3-morpholinopropyl)-2-phenylacetamide, exhibited excellent antitumor cell proliferative activity against multiple tumor cell lines. In the study of the antitumor mechanism of XS23, we confirmed that it can inhibit tumor cell migration and proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner in A375 cells. Besides, 5 μM of XS23 could induce 18% early cell apoptosis and 4.68% late cell apoptosis in A375 cells. XS23 can also dose-dependently and time-dependently increase cleaved the caspase-9 protein expression in A375 cells and increase the intracellular ROS level of A375 cells up to 175-fold compared with the negative control after 12 h, implying that XS23 can induce cancer cell apoptosis by elevating ROS production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...