A novel electrochemical sensor for determination of uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid and dopamine based on a carbon paste electrode modified with an electrochemically reduced para-nitrobenzoic acid/graphene oxide nanocomposite†
Abstract
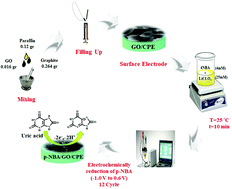
In this study, a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor based on a carbon paste electrode was modified by an electrochemically reduced para-nitrobenzoic acid/graphene oxide nanocomposite to measure uric acid. Field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were employed to characterize the modified electrode. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) methods were used to investigate the modified electrode for the electrocatalytic oxidation of uric acid in aqueous solutions. The effects of experimental parameters including pH and the scan rate were investigated using the uric acid cyclic voltammetry response. The highest peak current was obtained at pH = 7 with a diffusion-controlled mechanism. By using differential pulse voltammetry, the peak current was linearly dependent on the concentration of uric acid in the ranges of 0.1–54 μM and 54–600 μM with a detection limit of 48 nM (S/N = 3). It was demonstrated that the modified carbon paste electrode reported here is suitable for the determination of uric acid in real samples like human blood serum.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...