Benzimidazole-based ionic and non-ionic organoselenium compounds: innovative synthetic strategies, structural characterization and preliminary anti-proliferative activities†
Abstract
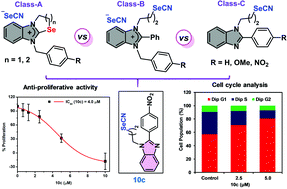
The design of and synthetic routes to three different classes of structurally innovative ionic (7a and 7b, 8a–8c and 9a–9c) and non-ionic organoselenium compounds (10a–10c) containing benzimidazole pharmacophores and substituted phenyl rings (4-H, 4-NO2 and 4-OMe) are described. The ionic sets of compounds consisted of benzimidazole-fused cyclic selenazolium selenocyanates (7a and 7b), selenazinium selenocyanates (8a–8c) and acyclic benzimidazolium selenocyanates (9a–9c). The final compounds could be synthesized effectively from the suitable benzimidazole derivatives in multi-step synthesis and the selenium incorporation was done using potassium selenocyanate. All the purified compounds were characterized by analytical methods and the structure of a representative selenazolium selenocyanate (7b) was further confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction study. A mechanistic outline was proposed for the cyclized products. Considering the hints about the anti-cancer and chemopreventive activities of reported organoselenocyanates, the innovative sets of synthesized ionic and non-ionic compounds were evaluated for their preliminary anti-proliferative activities against highly aggressive triple-negative breast cancer (MDA-MB-231, human breast adenocarcinoma) cells. Interestingly, our in vitro studies revealed the highly enhanced anti-proliferative activities of non-ionic organoselenocyanates over ionic organoselenium compounds in general and the significantly high selectivity of the lead compound 10c having the 4-NO2 group towards cancer cells over normal cells. The lead compound exhibited potent anti-migratory activity, induced dose-dependent cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase and modulated the expression levels of key cancer-marker proteins. Our results reveal that 10c exhibits anti-proliferative activity most likely by arresting cells in the G1 phase and by enhancing intracellular ROS levels in triple-negative breast cancer cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...