Hematite nanoparticles decorated nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/graphitic carbon nitride multifunctional heterostructure photocatalyst towards environmental applications†
Abstract
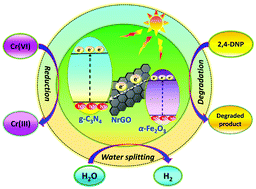
The carcinogenic heavy metals and aromatic organic compounds linger as wastewater pollutants implying a great menace to the ecological balance. To solve these environmental pollution problems, the photocatalytic process is an emerging technology. The present study demonstrates the fabrication of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles decorated nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide (NrGO)/graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanocomposite (NrGO/g-C3N4/α-Fe2O3: NGCF) for Cr(VI) photoreduction and 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) photodegradation. The prepared nanocomposites were also tested for photocatalytic hydrogen (H2) evolution activity under visible light irradiation. The physicochemical activity of the synthesized NGCF was evaluated, revealing that the ternary heterojunction nanocomposites were successfully formed. Among all the synthesized nanocomposites, NrGO/g-C3N4/α-Fe2O3-10 (NGCF-10) showed superior photocatalytic activity. The result manifested that about 95% of Cr(VI) reduction was achieved by NGCF-10 nanocomposite after 60 min of visible light exposure. Furthermore, about 88% of the catalytic degradation of DNP was reached after 70 min of visible light irradiation using NGCF-10 nanocomposite. Also, the NGCF-10 nanocomposite exhibited a higher H2 evolution rate of 633.92 μmol h−1 g−1, which was about 18.01 and 2.98 times greater than that of pristine g-C3N4 and NrGO/g-C3N4 (NGC). As a result, the synthesized NGCF nanocomposite could be an effective photocatalyst for removing both organic and inorganic pollutants from water. The nitrogen doping in reduced graphene oxide (rGO) was confirmed from Raman and XPS analyses. Again, the trapping experiment was carried out to investigate the key reactive species responsible for the photocatalytic reaction as well as the plausible mechanism. Finally, the Z-scheme charge transfer channelization mechanism was accepted for the enhanced performance of the NGCF photocatalytic system. Moreover, the reusability examination of NGCF nanocomposite revealed excellent stability and recyclability for up to five successive cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...