Facile fabrication of electrospun g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2/poly(acrylonitrile-co-maleic acid) heterojunction nanofibers for boosting visible-light catalytic ofloxacin degradation†
Abstract
Developing excellent photocatalysts for pollutant degradation is of vital significance but still a big challenge. In this work, an electrospun g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2/poly(acrylonitrile-co-maleic acid) (E-spun g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2/PANCMA) nanofiber photocatalyst was fabricated by coaxial electrospinning of g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2 and PANCMA and showed high adsorption capacity and excellent visible light catalytic degradation performance with the adsorption amount and degradation rate of antibiotic ofloxacin (OFL) as high as 4.44 mg g−1 within 6 min and 94% within 20 min, respectively. Compared to pure g-C3N4 and Bi12O17Cl2, the g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2 heterojunction showed higher visible light absorption and degradation ability, ascribed to the synergistic effect of g-C3N4 and Bi12O17Cl2 on the separation and utilization efficiency of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. E-spun g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2/PANCMA nanofibers exhibited highly efficient photocatalytic activity over a wide pH range of 4.0–8.0 and some interference of metal ions and inorganic anions, and the reactive species including holes (h+), superoxide radicals 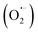 , and hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) all participated in the photocatalytic degradation of OFL. Moreover, the E-spun g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2/PANCMA possessed excellent cycling stability of 81.9% efficiency retention after fifteen consecutive tests. In addition, the possible degradation mechanism, intermediate products and degradation pathways of OFL were investigated by ESR tests, radical scavenger experiments, and LC-MS analysis. This study developed a feasible exemplificative strategy for fabricating new highly efficient and reusable photocatalyst candidate materials to remove environmental pollutants.
, and hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) all participated in the photocatalytic degradation of OFL. Moreover, the E-spun g-C3N4/Bi12O17Cl2/PANCMA possessed excellent cycling stability of 81.9% efficiency retention after fifteen consecutive tests. In addition, the possible degradation mechanism, intermediate products and degradation pathways of OFL were investigated by ESR tests, radical scavenger experiments, and LC-MS analysis. This study developed a feasible exemplificative strategy for fabricating new highly efficient and reusable photocatalyst candidate materials to remove environmental pollutants.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...