Catalytic degradation of methylene blue using iron and nitrogen-containing carbon dots as Fenton-like catalysts†
Abstract
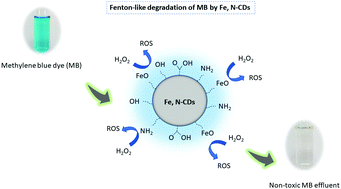
Wastewater pollution is an existing and serious environmental issue. One of the main wastewater pollution sources is from the dyestuff industries and its discharge poses a serious threat to the ecosystem due to its adverse effects on human and environmental health. Conventional wastewater treatments are limited in terms of effectively treating such non-biodegradable contaminants; thus, this work aimed to investigate the degradation of the commercial dye methylene blue (MB) via advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) using carbon dots as Fenton-like catalysts. Iron and nitrogen-containing carbon dots (Fe, N-CDs) were synthesised through a hydrothermal reaction and utilised as catalysts in the degradation of MB. Multiple characterisation techniques were employed to describe the dot properties including FTIR, XPS, TEM, ζ-potential, PL and UV-Vis analyses. Characterisation revealed the synthesis of 7 nm diameter, spherical negatively charged dots rich in iron and nitrogen surface functionalities. Methylene blue was degraded under mild conditions using an innovative green remediation technology which removed nearly 100% of the dye (20 mg L−1) under optimised conditions (at 50 °C, pH 8, H2O2 147 mM, and a catalyst concentration of 0.5 mg mL−1) in only 60 minutes. The active mechanism of the Fe, N-CDs was deduced suggesting the participation of free radicals such as hydroxyl radicals, singlet oxygens and holes. Importantly, the effluent toxicity assessed using Microtox® confirmed the generation of a non-toxic effluent. This investigation showed that using Fe, N-CDs is an effective way to degrade wastewater pollution whilst significantly minimising its toxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...