Non-volatile ternary memristors based on a polymer containing a carbazole donor with CuO NPs embedded
Abstract
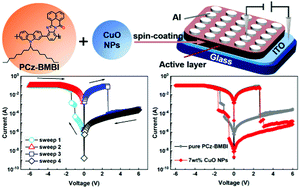
The limited capacity of binary memory may not meet the requirements of future information storage; hence, multilevel memory is widely studied. Herein, a donor–acceptor-type polymer poly[2,7-9-(heptadecan-9-yl)-9H-carbazole-alt-7H-benzimidazo[2,1-a]benz[de]isoquinolin-7-one] (PCz–BMBI) was synthesized using the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction and characterized. The organic resistive random access memory (ORRAM) devices with a non-volatile ternary memory behavior, based on PCz–BMBI and PCz–BMBI:CuO NP active layers, were fabricated using the spin-coating technique. The I–V characteristics of the devices were studied, and the effect of the embedding ratio of CuO nanoparticles (NPs) on the memory performance of the devices was discussed. The results indicate that the switching ratios of all devices with CuO NPs embedded were improved, and their first threshold voltages were lowered. Furthermore, the devices fabricated with an embedding ratio of 7 wt% CuO NPs exhibited optimal memory performance with a current ratio of ON2/ON1/OFF (105.3 : 102.3 : 1) and low threshold voltages (−0.50 V/−1.60 V). This work provides a new route for multi-level storage materials and new ideas for the application of CuO NPs in the field of information storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...