Cell penetrating peptide (CPP) gold(iii) – complex – bioconjugates: from chemical design to interaction with cancer cells for nanomedicine applications†
Abstract
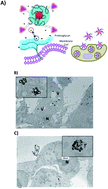
This study promotes an innovative synthesis of a nanotheragnostic scaffold capable of targeting and destroying pancreatic cancer cells (PDAC) using the Biotinylated NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide (BIOT-NFL), known to enter various glioblastoma cancer cells (GBM) where it specifically destroys their microtubule network. This recently proposed methodology (P7391FR00-50481 LIV) applied to other peptides VIM (Vimentin) and TAT (Twin-Arginine Translocation) (CPP peptides) has many advantages, such as targeted selective internalization and high stability under experimental conditions, modulated by steric and chemical configurations of peptides. The successful interaction of peptides on gold surfaces has been confirmed by UV-visible, dynamic light scattering (DLS), Zeta potential (ZP) and Raman spectroscopy analyses. The cellular internalization in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC; MIA PACA-2) and GBM (F98) cells was monitored by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and showed a better cellular internalization in the presence of peptides with gold nanoparticles. In this work, we also evaluated the power of these hybrid peptide-nanoparticles as photothermal agents after cancer cell internalization. These findings envisage novel perspectives for the development of high peptide-nanotheragnostics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...