Long-read 16S-seq reveals nasopharynx microbial dysbiosis and enrichment of Mycobacterium and Mycoplasma in COVID-19 patients: a potential source of co-infection†
Abstract
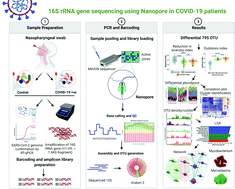
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a major global health concern. This virus infects the upper respiratory tract and causes pneumonia-like symptoms. So far, few studies have shown alterations in nasopharyngeal (NP) microbial diversity, enrichment of opportunistic pathogens and their role in co-infections during respiratory infections. Therefore, we hypothesized that microbial diversity changes, with increase in the population of opportunistic pathogens, during SARS-CoV2 infection in the nasopharynx, which may be involved in co-infection in COVID-19 patients. The 16S rRNA variable regions, V1–V9, of NP samples of control and COVID-19 (symptomatic and asymptomatic) patients were sequenced using the Oxford Nanopore™ technology. Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis for determining alpha/beta diversities, non-metric multidimensional scaling, correlation studies, canonical correspondence analysis, linear discriminate analysis, and dysbiosis index were used to analyze the control and COVID-19-specific NP microbiomes. We observed significant dysbiosis in the COVID-19 NP microbiome with an increase in the abundance of opportunistic pathogens at genus and species levels in asymptomatic/symptomatic patients. The significant abundance of Mycobacteria spp. and Mycoplasma spp. in symptomatic patients suggests their association and role in co-infections in COVID-19 patients. Furthermore, we found strong correlation of enrichment of Mycobacteria and Mycoplasma with the occurrences of chest pain and fever in symptomatic COVID-19 patients. This is the first study from India to show the abundance of Mycobacteria and Mycoplasma opportunistic pathogens in non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients and their relationship with symptoms, indicating the possibility of co-infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...