Abstract
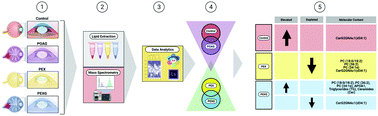
Pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PEX) is a systemic disorder that manifests as a fluffy, proteinaceous fibrillar material throughout the body. In the eye, such deposits result in glaucoma (PEXG), due to impeding aqueous humor outflow. Serum lipid alterations and increased lipid peroxidation have been reported in PEX. We report the first ever comprehensive lipid profiling of the aqueous humor (AH) of PEXG. Our untargeted lipidomic analysis of 23 control, 19 primary open angle glaucoma (POAG), 9 PEX, and 14 PEXG AH patients resulted in the identification of 489 lipid species within 26 lipid classes across PEX, PEXG, POAG, and control AH samples. Multiple cholesterol esters (ChEs), phosphatidylcholines (PCs), triglycerides (TGs), and ceramides (Cers) were present in higher concentrations in the PEXG AH than in all other groups. CerG2GNAc1(d34 : 1) was enriched in control samples and depleted in both the PEX and PEXG samples. Machine learning prediction with three supervised logistic regression binary classification tasks showed (1) POAG vs. control, with an 86% accuracy, (2) PEXG vs. control, with a 71% accuracy and (3) PEX vs. control, with an 86% accuracy. In conclusion, the analysis showed that the control (mean peak area 13.54 ± 6) had, on average, a higher total lipid content than the PEX, PEXG, and POAG AH samples. Elevations in Apolipoprotein A-I (APOA1) correlated with an increased abundance of PC lipid species in the AH of patients with PEXG. PC (18 : 0/18 : 2), PC (36 : 2), and PC (34 : 1e) are in low concentrations for PEX but are highly concentrated in PEXG, despite both having similar material deposits, suggesting that they are fundamentally different in composition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...