Research progress on nano-sensitizers for enhancing the effects of radiotherapy
Abstract
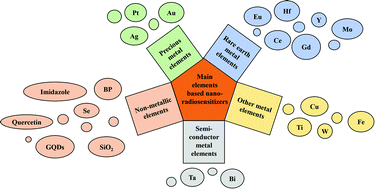
Radiotherapy (RT) is local control of tumors using radiation, including external irradiation (EBRT) and internal irradiation (RIT). Cancer radiotherapy based on external beams is a major clinical treatment for cancer, which has been widely used in the treatment of more than one-third of local solid tumors. However, due to the tumor's insensitivity to radiation, low absorption rate of radiation by tumors, large radiation doses are often needed during radiotherapy, causing serious damage to normal tissues near the tumors. The most important is that the extent of cancer cell damage caused by radiotherapy and the radiosensitivity of tumors is mainly determined by the concentration of oxygen. The above two aspects severely limit the effect of radiotherapy. Nano-sensitizers can effectively accumulate radiation doses and enhance radiation effects, thereby improving the efficacy of radiotherapy. In addition, nano-sensitizers can also increase tumor sensitivity to radiation through reactive oxygen species (ROS). Therefore, this article reviews the latest progress of nano-sensitizers for radiotherapy, which is focused on precious metal-based nano-sensitizers, rare earth metal-based nano-sensitizers, semiconductor metal-based nano-sensitizers, other metal- and nonmetal-based nano-sensitizers. And the recent literature reports and applications of the nano-sensitizers are also discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...