Photophysical, electrochemical properties and flexible organic solar cell application of 7,7-bis(1-cyclopropyl carbonyl piperazino)-8,8 dicyanoquinodimethane†
Abstract
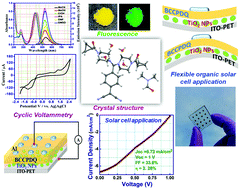
Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ), when reacted with primary/secondary/simple aromatic amines, generates mono/di-substituted derivatives, predominantly manifesting in optical/non-linear optical properties. Nevertheless, the utilization of specific amines plays a critical role in terms of the materials aspects emerging from the diverse range of structures and unforeseeable properties. Surprisingly, demonstration of a TCNQ derivative with a simple, small amine moiety, emerging in organic solar cell applications has so far remained unexplored. Moreover, a knowledge gap still exists in terms of TCNQ derivatives. Accordingly, a thermally stable 7,7-bis(1-cyclopropylcarbonyl piperazino)-8,8-dicyanoquinodimethane (BCCPDQ) fluorophore was successfully attained in a one-step effortless synthesis using 1-(cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazine. Solid BCCPDQ displays enhanced fluorescence (Φf = ∼10%) compared to in solution (Φf = ∼0.30%). The electrochemical band gap (∼2.67 eV) was found to be in good agreement with the optical band gap (∼2.68 eV). Furthermore, BCCPDQ exhibits organic flexible solar cell device capability, noted for the first time among TCNQ derivatives. The heterostructure device embedded with TiO2 nanoparticles tested for various photovoltaic (PV) parameters displays excellent stability, with an efficiency of around 2.26%. The electrical characteristics of the device on a flexible substrate did not degrade under various bending conditions, and the acquired findings correspond well with the zero stress device, demonstrating the exceptional stability of the PV and its potential for use in wearable and flexible electronics. To gain a greater understanding on the mechanism involved, the PV characteristics were described using a band diagram. Consequently, this study represents a cutting-edge method in understanding a new tiny organic molecular material and integrating it into a flexible solar cell.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...