Shear and endothelial induced late-stage calcific aortic valve disease-on-a-chip develops calcium phosphate mineralizations†
Abstract
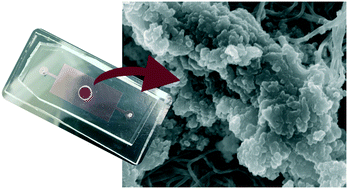
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is an active pathobiological process leading to severe aortic stenosis, where the only treatment is valve replacement. Late-stage CAVD is characterized by calcification, disorganization of collagen, and deposition of glycosaminoglycans, such as chondroitin sulfate (CS), in the fibrosa. We developed a three-dimensional microfluidic device of the aortic valve fibrosa to study the effects of shear stress (1 or 20 dyne per cm2), CS (1 or 20 mg mL−1), and endothelial cell presence on calcification. CAVD chips consisted of a collagen I hydrogel, where porcine aortic valve interstitial cells were embedded within and porcine aortic valve endothelial cells were seeded on top of the matrix for up to 21 days. Here, we show that this CAVD-on-a-chip is the first to develop human-like calcified nodules varying in calcium phosphate mineralization maturity resulting from high shear and endothelial cells, specifically di- and octa-calcium phosphates. Long-term co-culture microfluidic studies confirmed cell viability and calcium phosphate formations throughout 21 days. Given that CAVD has no targeted therapies, the creation of a physiologically relevant test-bed of the aortic valve could lead to advances in preclinical studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...