High spectral stability and quantitative accuracy of LIBS by optimization of a combined atomic and ionic line algorithm†
Abstract
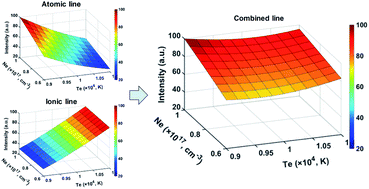
Large spectral fluctuations bring about large errors in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) analysis, which impedes the improvement of precision and accuracy, limiting its large-scale application and commercialization. In this work, we proposed an improved algorithm based on the optimization of a combined atomic and ionic line algorithm. The principle of the optimized algorithm was explained and verified by simulation. Then ferrum (Fe) and manganese (Mn) in aluminum bronze and two series of soil samples were applied. In the aluminum bronze samples, the average RSDs of line intensities were reduced from 7–15% of atomic and ionic lines to 5–8% of combined lines. The average R2 values of the calibration curves were improved from 0.982 and 0.992 of single line calibration to 0.991 and 0.996 of combined line calibration for Mn and Fe, respectively. And the average RMSECVs decreased from 0.243% and 0.171% to 0.208% and 0.135% for Mn and Fe, respectively. Similar improvements were also found in the soil samples. The results further proved the effectiveness and feasibility of the optimized combined line algorithm in improving the spectral stability and quantitative accuracy, which is of benefit to the further promotion and commercialization of LIBS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...