Designing and screening of fluoroquinolone substitutes using combined in silico approaches: biological metabolism–bioconcentration bilateral selection and their mechanism analyses†
Abstract
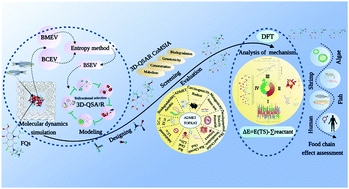
The study was aimed to design fluoroquinolone (FQ) substitutes, improve the biological metabolism and concentration ability of fluoroquinolones (FQs) drug from the perspective of source control, and provide theoretical support for alleviating the potential environmental risks of FQs. First, the 3D-QSA2R model of the bidirectional selective effect of FQs was constructed, and 122 norfloxacin (NOR) substitutes were designed. Then, the biological metabolism and concentration of the 3D-QSAR models, two environmental friendliness evaluation models, and the pharmacokinetics (ADMET) and toxicokinetics (TOPKAT) models were used for screening, evaluation, and verification. Moreover, three environment-friendly NOR substitutes (N-039, N-068, and N-120) with enhanced bidirectional selectivity, improved functional properties and reduced human health and ecological risk were screened. Finally, the simulation of the metabolic pathways of the three molecules in fish was established. Meanwhile, their metabolic capacity in organisms of different trophic levels in the food chain (algae → shrimp → fish → human) was evaluated. Additionally, based on molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, and notability analysis, it was found that van der Waals force was the dominant factor in the enhancement of the bio-metabolism of FQs, NOR substitutes entered the catalytic active sites of metabolic enzymes more easily than NOR, and more hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic bonds were formed to improve the metabolic transformation ability of molecules in aquatic organisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...