The choice of ionic liquid ions to mitigate corrosion impacts: the influence of superbase cations and electron-donating carboxylate anions†
Abstract
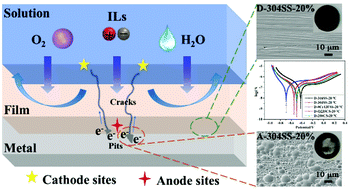
Ionic liquids (ILs) including novel superbase-derived ILs and imidazolium-based ILs with the potential to be used as green solvents for biomass utilization should be deeply evaluated with respect to their corrosion ability towards metallic equipment in industrialization. Herein, the corrosion susceptibility of 304SS in [DBUH][CH3CH2OCH2COO] was investigated for the first time and compared with that in common [EMIM][Ac] and [AMIM][Cl] by electrochemical, surface, and theoretical analyses. [DBUH][CH3CH2OCH2COO] exhibited an unprecedentedly excellent corrosion inhibition for 304SS compared to imidazolium-based ILs. This may be due to the presence of electron-donating carboxylate anions and macrocyclic superbase cations, which reacted with metals to form a compact layer and protected metals from damage. [EMIM][Ac] showed a slightly unfavorable corrosion inhibition compared to [DBUH][CH3CH2OCH2COO]. However, the corrosion rate of 304SS was dramatically increased in [AMIM][Cl] by increasing the temperature and water contents, which was reflected by pitting corrosion with plenty of pits (5–10 μm in diameter) on the 304SS surface after a polarization test. By studying the corrosion behaviour of five common steels in [DBUH][CH3CH2OCH2COO] and taking economy into consideration, 304SS with high Rct (26.69 × 105 Ω cm2) and Rp values (1230.8 Ω cm2) was the top priority for industrial equipment materials. According to the possible corrosion mechanism of metals in ILs from the viewpoint of DFT calculations and complex physico-chemical interactions, carboxylate ILs displaying outstandingly low contributions to corrosion particularly involving superbase cations or imidazolium cations and carboxylate anions with electron-donating groups such as –OCH2CH3, –OCH3, and –HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 should be designed to mitigate corrosion damage in industrialized operations.
CH2 should be designed to mitigate corrosion damage in industrialized operations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...