Multi-step chemo-enzymatic synthesis of azelaic and pelargonic acids from the soapstock of high-oleic sunflower oil refinement†
Abstract
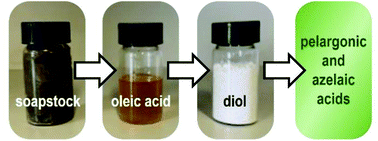
Soapstock recovery and manipulation represent one of the most burdensome aspects of the vegetable seed oil refining industry. In particular, soapstock splitting requires high amounts of concentrated acid and produces a low-value mixture of triglycerides and free fatty acids (oleins or acid oil), as well as huge volumes of acidulated wastewater. Oleins are currently converted into biodiesel or supplied to biodigesters, but alternative procedures to afford high-value products are sought after by the vegetable seed oil industry. In this paper, the valorization of soapstock from high-oleic sunflower oil refinement is investigated by biocatalytic methods. First, lipases are used to catalyze an efficient soapstock splitting, and reduce the environmental load of the procedure. Then, the high content of oleic acid (60–80%) is exploited by promoting its oxidative cleavage. Self-epoxidation of oleic acid by lipase-mediated perhydrolysis in the presence of H2O2 affords the corresponding epoxide, which is subsequently hydrolyzed to the diol derivative and oxidized to commercially valuable azelaic and pelargonic acids. The cleavage is performed using only sodium hypochlorite as an inexpensive and efficient oxidant. Epoxidation and glycol cleavage are optimized by a statistical approach and implemented under continuous-flow conditions to increase yields and productivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...