Formation of Amadori compounds in LIGAO (concentrated pear juice) processing and the effects of Fru-Asp on cough relief and lung moisturization in mice†
Abstract
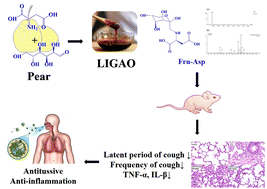
LIGAO (concentrated pear juice) has been used for more than 1000 years to treat respiratory complaints such as cough and expectoration in China, but the study of the mechanism of its antitussive effects and ability to moisten the lungs is limited. This study found that the content of Amadori compounds (ACs) and other nutrients changed during LIGAO processing. Furthermore, N-(1-deoxy-D-fructos-1-yl)-aspartic acid (Fru-Asp), the most abundant and characteristic AC in LIGAO, was prepared and studied. The antitussive test revealed that Fru-Asp could significantly reduce the frequency of cough and prolong the cough latent period in mice. A high dose of Fru-Asp (250 mg kg−1) in mice provided better therapeutic activities than that of dextromethorphan hydrobromide tablets (30 mg kg−1). In the Fru-Asp pretreated group, Fru-Asp significantly alleviated inflammation in LPS-induced acute lung injury mice. Fru-Asp can significantly decrease the levels of TNF-α and IL-β in mice by 11%. Additionally, Fru-Asp exhibited angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor activity (IC50 = 0.242 mM). The contribution and health benefits of Fru-Asp on cough relief were first reported in this study, which also substantiated it as a functional component of LIGAO. The results provided the basis for future research on the health effects of ACs and a method to improve the added value of LIGAO and other pear products.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...