Potential protective mechanism of Tibetan kefir underlying gut-derived liver injury induced by ochratoxin A†
Abstract
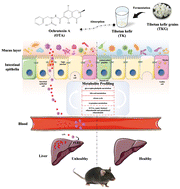
Tibetan kefir (TK) is a good source of probiotics and has antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and gut microbiota-regulating properties. Ochratoxin A (OTA) causes liver injury through the gut microbiota. It is unclear whether TK has differential effects on the gut–liver axis and whether these effects can alleviate liver injury induced by OTA. Herein, we investigated the hepatoprotective effect of TK in OTA-fed mice and its underlying mechanisms in the context of the gut. The results indicate that microorganisms in TK bound to OTA and decreased its gastrointestinal absorption. TK improved the intestinal barriers, and suppressed oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Moreover, TK supplementation alleviated the gut microbiota dysbiosis by enriching beneficial microbiota such as Akkermansia and Lachnospiraceae UCG-006, and reducing harmful bacteria. Importantly, TK supplementation reversed the liver injury by reducing gut leakage of Bacteroides and lipopolysaccharides. Furthermore, untargeted metabolomics revealed that TK reversed the perturbation of metabolites involved in glycerophospholipid and bile acid metabolism, and regulated metabolites that are pertinent to the citrate cycle and tryptophan metabolism. TK also increased the production of short-chain fatty acids and anti-inflammatory metabolites. These data are consistent with the protective effects of TK against OTA-induced liver injury by maintaining the intestinal barrier and modulating the gut microbiota and metabolites. These findings will facilitate therapeutic interventions for mycotoxicosis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...