UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MSE-based metabolomics analysis of Acer mono sap and evaluation of osteogenic activity in mouse osteoblast cells†
Abstract
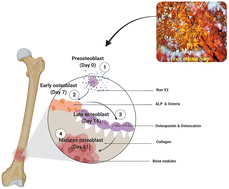
Investigation of phytochemicals and bioactive molecules is tremendously vital for the applications of new plant resources in chemistry, food, and medicine. In this study, the chemical profiling of sap of Acer mono (SAM), a Korean syrup known for its anti-osteoporosis effect, was performed using UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MSE analysis. A total of 23 compounds were identified based on the mass and fragmentation characteristics and most of the compounds have significant biomedical applications. The in vitro antioxidant assessment of SAM indicated excellent activity by scavenging DPPH and ABTS-free radicals and were found to be 23.35 mg mL−1 and 29.33 mg mL−1, respectively, as IC50 concentrations. As well, the in vitro proliferation effect of the SAM was assessed against mouse MC3T3-E1 cells, and the results showed that the SAM enhanced the proliferation of the cells, and 12.5 mg mL−1 and 25 mg mL−1 of SAM were selected for osteogenic differentiation. The morphological analysis clearly evidenced the SAM enhanced the osteogenic activity in MC3T3-E1 cells by the increased deposition of extracellular calcium and nodule formation. Moreover, the qRT-PCR analysis confirmed the increased expression of osteoblast marker gene expression including ALP, osteocalcin, osteopontin, collagen1α1, Runx2, and osterix in SAM-treated MC3T3-E1 cells. Together, these results suggest that SAM possesses osteogenic effects and can be used for bone regeneration and bone loss-associated diseases such as osteoporosis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...