Improving the gastrointestinal activity of probiotics through encapsulation within biphasic gel water-in-oil emulsions
Abstract
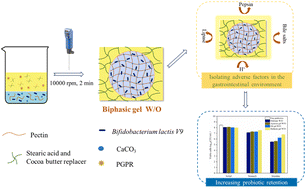
The development of probiotics encapsulation strategies has always been a hot topic due to the high sensitivity of probiotics to processing, storage and the gastrointestinal environment. In this study, water in oil (W/O) emulsions of single-phase or dual-phase gels were constructed through the water phase, oil phase alone or all gels. And the W/O emulsions were used to encapsulate Bifidobacterium lactis V9. The effects of water, oil and biphasic gels on the physicochemical properties of the emulsion and the probiotic activity were investigated. Water, oil and biphasic gels contribute to the stability of emulsions. Oil-phase gels make the emulsion form a solid-like texture, while water-phase gels have no significant effect on the liquidity of the emulsion. The microscopic image shows that the probiotics were completely encapsulated in the internal aqueous phase due to the excellent water affinity of probiotic powder. In addition, all W/O emulsions retain higher probiotic activity, which is attributed to good physical isolation during the gastric phase, while oil-phase and biphasic gel emulsions have high probiotic activity after intestinal digestion due to reduced lipid digestion by oil-phase gels. A liquid or solid-state encapsulated probiotic emulsion has been developed and can be used as a coating sauce, solid fat, etc., which can provide additional ideas for probiotic encapsulation systems and functional food development.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...