Surface modified porous silicon with chitosan coating as a pH-responsive controlled delivery system for lutein†
Abstract
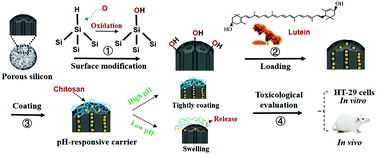
Surface modified pH-responsive porous silicon (PSi) carriers were developed for efficient delivery of lutein. PSi particles were prepared by the electrochemical etching method and modified with two chemical groups: hydroxyl and octadecyl silane, respectively. Chitosan (CS) was used for coating of PSi to ensure pH-responsive release. The loading conditions, release properties, cytotoxicity and toxicity were investigated. The highest loading percentage of lutein could be obtained with oxidized PSi and the structure of the microparticles was characterized by Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy. The surface area and pore size of the microparticles were obtained from the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm. The CS–PSi–Lut microparticles showed the minimum surface area of 220.30 m2 g−1 and a relatively larger average pore width of 179.00 Å. In vitro release experiments showed a pH-responsive and controlled release of lutein, with the fastest release rate and highest cumulative release rate of 97% under acidic conditions (pH 5.0) within 7 h. PSi, chitosan and lutein showed synergistic toxic effects, and the CS–PSi–Lut microparticles could effectively inhibit the proliferation of HT-29 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with an inhibition rate of 77% when the lutein concentration reached 40 μg mL−1. The in vivo toxicological evaluation of CS–PSi–Lut microparticles indicated good biocompatibility in the range of experimental doses. The chitosan-coated oxidized PSi capable of delivering bioactive compounds in a targeted and controlled manner provides a novel platform for the development and application of lutein.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...