Effects of probiotic supplementation on glucose metabolism in pregnant women without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis†
Abstract
Background: The preventive effects of probiotic supplementation against gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in pregnant women remain unclear. The objective of this review was to investigate the effect of probiotic supplementation on the profiles of glucose metabolism in pregnant women without diabetes. The published literature was retrieved and screened from PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure), Wanfang, and Cochrane Center Register of Controlled Trails up to April 1st, 2021. Random controlled trials (RCTs) of probiotic supplementation on pregnant women without GDM were included. Results: 12 RCTs (2213 participants) were eligible for meta-analyses. Overall, probiotic supplementation significantly reduced GDM incidence (Risk Ratio (RR) = 0.62, 95% CI: 0.39–0.99), serum fasting blood glucose (FBG) (Mean Difference (MD) = −0.14 mmol L−1; 95% CI: −0.26 mmol L−1, −0.01 mmol L−1), insulin concentration (MD = −1.91 pmol L−1, 95% CI: −2.41 to −1.41), the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (MD = −0.32 mmol L−1; 95% CI: −0.42 mmol L−1, −0.22 mmol L−1), and Quantitative Insulin sensitivity Check Index (QUICKI) (MD = 0.02, 95% CI: 0.01,0.03) in pregnant women. Probiotic supplementation had no significant effects on the results of the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) (1 h OGTT, MD = −0.10, 95% CI: −0.30, 0.09; 2 h OGTT, MD = −0.06, 95% CI: −0.31, 0.20). Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggested that probiotic supplementation may lead to an improvement in glycemic control and reduction of GDM incidence in pregnant women.
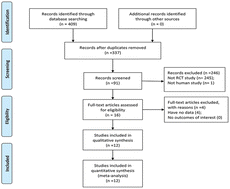


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...