Soybean diacylglycerol regulates lipid metabolism in d-galactose-induced aging rats by altering gut microbiota and gene expression of colonic epithelial cells†
Abstract
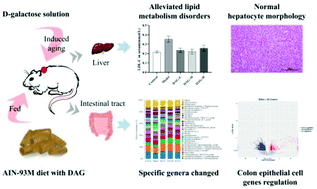
Lipid metabolism is closely related to the health of aging bodies and its disorder often leads to cardiovascular diseases and chronic diseases. Dietary fat is one of the important sources of body fat, which affects the body's lipid metabolism. However, how dietary fat affects lipid metabolism in aging bodies has not been reported. Thus, the effects of soybean diacylglycerol (DAG) on lipid metabolism in D-galactose-induced aging rats were investigated by detecting the serum biochemical indexes, hepatocyte morphology, gut microbiota changes, and gene expression of colonic epithelial cells. The results showed that DAG alleviated the lipid metabolism disorders, and the hepatocyte morphology of aging rats fed DAG was normal. 16S rDNA analysis showed that DAG restored Eisenbergiella and Veillonella that were missing in aging rats. The relative abundances of Romboutsia and Ruminococcus_2 decreased and the relative abundance of Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group increased significantly with the influence of DAG (P < 0.05). Gene expression profiles showed that the gene expression of colon epithelial cells was altered by DAG and DAG downregulated the genes Lipe and Fabp4 related to the lipolysis of adipocytes. In conclusion, DAG regulated the lipid metabolism of aging rats by regulating gut microbiota and gene expression of colonic epithelial cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...