Platycodon grandiflorum root fermentation broth reduces inflammation in a mouse IBD model through the AMPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway†
Abstract
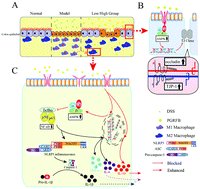
The effect of Platycodon grandiflorum (PG) on colitis and its underlying mechanism were rarely studied. In this study, Lactobacillus rhamnosus 217-1 was used to ferment PG roots, and the concentrations of platycodin-D, flavonoids, and polyphenols and the DPPH free radical scavenging rate were significantly increased. Treatment with a PG root fermentation broth (PGRFB) could reduce dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) induced ulcerative colitis (UC) in mice. Meanwhile, the PGRFB significantly reduced the content of inflammatory factors in mouse serum and the expression of inflammatory factor mRNA in the intestinal tract, regulated the polarization of M1/M2 macrophages, and increased the expression of tight junction protein mRNA in intestinal epithelial cells. In summary, it was proved that the PGRFB could inhibit the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway and the expression of Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and lowering the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...