l-Theanine mediates the p38MAPK signaling pathway to alleviate heat-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in mice†
Abstract
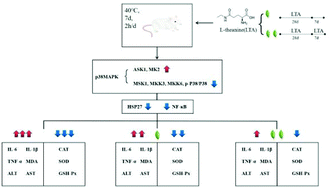
L-Theanine, an active ingredient in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis) associated with calming, is widely used as a functional ingredient and dietary supplement. In this study, a heat stress mouse model was used to evaluate the anti-heat stress effect of L-theanine and its possible mechanism of action. Mice subjected to heat stress (40 °C) that were administered L-theanine at various doses (100, 200, and 400 mg kg−1 d−1) had reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory factors when L-theanine was administered both long-term and as a preventative treatment. Our L-theanine intervention countered the reduction in growth and feed intake of mice under heat stress and reversed liver and jejunum tissue damage. Moreover, L-theanine countered the increase in inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β and antioxidant enzymes SOD and CAT; it also counteracted GSH-Px inactivation, the upregulation of AST and ALT enzyme activity, and MDA production. The mechanism of action may involve mediation of the P38 signaling pathway, inhibition of MK2 overexpression, and downregulation of p-P65/P65 caused by the overexpression of downstream HSP27. This would inhibit the heat stress-induced imbalance in oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...