Fabrication of a graphene oxide-embedded separation bilayer composite nanofiltration membrane using a combination of layer-by-layer self-assembly and interfacial polymerization†
Abstract
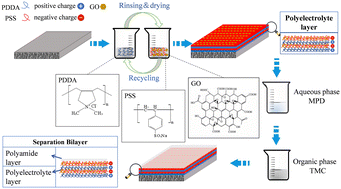
Layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly combined with interfacial polymerization (IP) was utilized to prepare a separation bilayer composite nanofiltration (NF) membrane containing a polyelectrolyte (PE) sub-layer and a polyamide (PA) top-layer. Graphene oxide (GO) was embedded in the PE layer to further modify the NF membrane properties. A filtration experiment demonstrated that the permeability of 2 g L−1 MgSO4 solution through a (PE + GO)2.5–PA membrane was 4.46 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, which was 2.2 times that of a PA membrane and 1.3 times that of a PE2.5–PA membrane. Accordingly, it is inferred that PE and GO can improve the NF membrane performance as a PE layer increases the negative charge density of the membrane surface, and the retention of inorganic ions by the membrane is enhanced. During the LbL self-assembly process, GO with a two-dimensional lattice structure and strong hydrophilicity formed stacked layers, which not only improved the NF membrane retention but also provided excess water channels. With the reinforcement of the electrostatic repulsion effect, the modified NF membrane also showed good separation performance for a persistent organic pollutant, i.e., perfluorooctanoic acid. Based on analyses of morphology, charge, hydrophilicity, membrane-foulant adhesion force and flux decline during humic-acid fouling, the excellent antifouling ability of the (PE + GO)2.5–PA membrane was investigated. It was found to be mainly due to elevated hydrophilicity, negative charge and fewer adsorption sites. This study provides a demonstration of the effective combination of two different membrane preparation methods, as well as a method using carbon-based nanomaterials to prepare high-permeability, high-retention antifouling NF membranes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...