Shower water usage in Kruger National Park tourist accommodation: effectiveness of technology and information intervention to reduce use†
Abstract
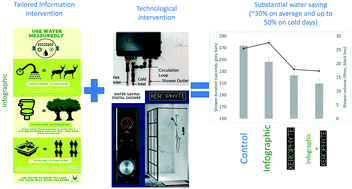
Human freshwater consumption continues to be a growing global concern. Research and implementation of interventions on multiple fronts are required to safeguard this critical resource. Household water consumption is a significant contributor to overall freshwater use. Such indoor water use in nature-based tourism presents a challenge to this industry, but also provides opportunities to influence human behaviour and experimenting with, and mainstreaming, new technologies promoting water conservation and sustainability. Here we assess interventions to one significant source of water use (showers) in tourist accommodation in a popular nature-based tourism destination, the Kruger National Park, South Africa. Control trials utilizing information interventions (to induce behavioural change), and a novel shower technology, are implemented to identify water saving opportunities. We show that technological intervention (installation of Triton Xerophyte®) results in ∼30% overall water saving as compared to control showers. Adding water-saving infographics slightly enhances this saving, but is shown to have limited success when implemented in isolation (i.e. without the technology). In addition, we show how shower duration and water usage is related to ambient temperature, with the Triton Xerophyte® resulting in increasing water savings under cooler ambient conditions (up to ∼50% water reduction for ambient temperatures <5 °C). Encouragingly, visitors to this national park are shown to use less shower water and shower for shorter, even in control units, as compared to the general public, suggesting that these nature-based tourists may already be more mindful of water usage. Nature-based tourism agencies have a responsibility to promote water saving behaviour, and implementing technology and providing information and awareness in aid thereof may act as a catalyst for broader water-conservation in society.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...