Efficient capture of phosphate from wastewater by a recyclable ionic liquid functionalized polyacrylonitrile fiber: a typical “release and catch” mechanism†
Abstract
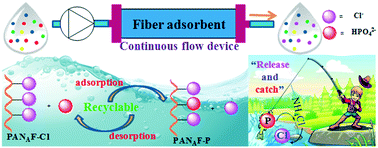
The enrichment and separation of phosphorus-containing compounds from wastewater can prevent eutrophication and can be used to recycle non-renewable resources. Herein, we developed a recyclable functionalized polyacrylonitrile fiber (PANAF–Cl) capable of loading an ionic liquid to adsorb phosphate in water. The results demonstrated that the PANAF–Cl reached the adsorption equilibrium within 5 min, with a maximum phosphate adsorption capacity of 15.49 mg P g−1. The fiber exhibited a wide range of pH adaptability with maximum adsorption capacity at the pH value of 5. A pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm model could better fit the adsorption of phosphate by the PANAF–Cl, indicating that the adsorption process belongs to monolayer chemisorption. Furthermore, the PANAF–Cl retains its considerable phosphate removal ability when Cl−, NO3−, etc. coexisting ions are included. It also exhibited a low adsorption limit (0.0184 mg P L−1) in actual wastewater and can be recycled at least 5 times. Moreover, the fiber revealed a high removal efficiency of above 90% for phosphate in simulated wastewater under continuous flow conditions. Besides, a “release and catch” ion exchange adsorption mechanism of PANAF–Cl for phosphate is proposed. Altogether, this study concludes that PANAF–Cl as an efficient phosphate adsorbent has high practical value for phosphate recovery and water purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...