The UV-B protective effect of a SiO2 doped TiO2 thin film regulates pitx3 and sparc expression during embryonic development of zebrafish
Abstract
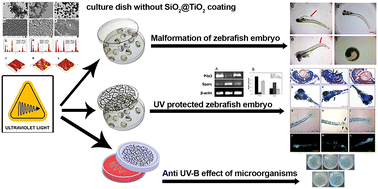
SiO2@TiO2 thin film synthesis and their UV protective application in microorganisms and the molecular response in the embryonic development of zebrafish were elucidated. SiO2@TiO2 thin films were fabricated on glass substrates by the sol–gel dip-coating technique. The UV screening effects of SiO2@TiO2 thin films as a protective layer to enhance the growth of Pseudomonas sp. and Azospirillum sp. were studied. We also observed that the survival rate and development of embryos of zebrafish increase with the increase in film thickness after UV exposure compared to the control. UV-B induced damage was observed in the development of eyes, cartilages, bones and fins of zebrafish. To elucidate the molecular mechanism involved, the expression of the pitx3 and sparc (osteonectin) genes was studied in UV-B exposed and SiO2@TiO2 thin film protected groups. The results indicated that pitx3 expression decreased and sparc expression increased under UV-B exposure. The expression level of the pitx3 and sparc genes was studied in the SiO2@TiO2 thin film protected group and compared to the control to determine the UV-B protective effect of SiO2@TiO2 thin films in the embryonic development of zebrafish. In conclusion, SiO2@TiO2 thin films act as a protective screen against UV-B radiation which may be useful for biomedical and agricultural applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...