Aggravated toxicity of copper sulfide nanoparticles via hypochlorite-induced nanoparticle dissolution†
Abstract
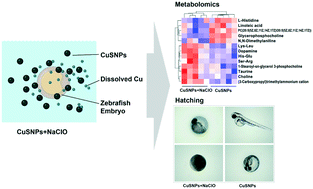
Sulfidation has been considered as a primary detoxification process for metal and metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs). Copper sulfide nanoparticles (CuSNPs) are deemed relatively non-toxic to aquatic wildlife due to their low solubility in water. However, dissolution of CuSNPs in water with hypochlorite, a common disinfectant used for wastewater treatment, may potentiate risks to aquatic life and humans. We therefore measured the effect of hypochlorite disinfection on the chemical stability of CuSNPs and assessed the aggravated toxicity of CuSNPs via hypochlorite-induced NP dissolution. Our results revealed that the chemical stability of CuSNPs was reduced through hypochlorite oxidation. Subsequently, the dissolved copper became more bioavailable in zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos were not impacted by CuSNPs at an environmental-related level, while the mixture exposure of CuSNPs and hypochlorite induced significant developmental toxicity in early staged zebrafish. The aggravated toxicity of the mixture of CuSNPs and hypochlorite in zebrafish embryos through induction of oxidative stress and membrane damage was confirmed by both metabolomics and in vivo experiments. Our findings demonstrate that CuSNPs may have aggravated toxicity to aquatic organisms through hypochlorite-induced NP dissolution and highlight that the impact of the transformation of NPs in the water treatment process should be considered when studying nanotoxicology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...