Screening of pesticide distributions in foods of animal origin: a matrix-based approach for biotransfer factor modeling of grazing mammals†
Abstract
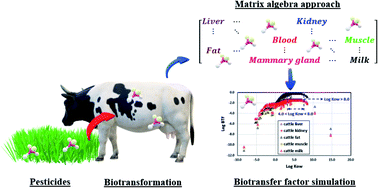
Pesticides are detected in a wide array of foods of animal origin, posing a threat to food safety and human health. Here, to facilitate the management of pesticide residues in livestock products, we proposed a screening model for simulating pesticide biotransfer factors (BTFs, ratio of steady-state pesticide concentration between animal tissues and feed) in mammalian bodies. The proposed model was developed based on simple matrix algebra using first-order kinetics. Simulation of over 700 pesticides in common food products derived from cattle and sheep indicated that pesticide biotransfer is a balancing process between uptake efficiency from the gut lumen and the uptake-elimination ratio (ratio of the overall uptake and elimination rate constants) in individual tissues. Furthermore, we parameterized the developed BTF model using the octanol–water partition coefficient. The simulated pesticide BTFs could be categorized into three lipophilicity phases, namely, the lipophilicity-boosting (log KOW < 4), lipophilicity-balancing (4 ≤ log KOW ≤ 8), and lipophilicity-limiting (log KOW > 8) phases, and the simulated general trends of BTFs were consistent with the experimental data. Although the metabolic rate constants of pesticides in mammalian bodies warrant further evaluation, the model proposed here can assist in the risk assessment and regulatory management of pesticide residues in foods of animal origin.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Recent Open Access Articles and Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...