Co-intercalation-free ether electrolytes for graphitic anodes in lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
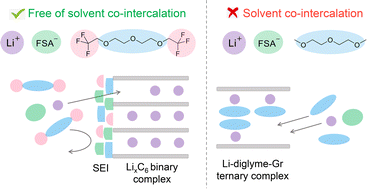
Carbonate-based electrolytes are widely used in Li-ion batteries but are limited by a small operating temperature window and poor cycling with silicon-containing graphitic anodes. The lack of non-carbonate electrolyte alternatives such as ether-based electrolytes is due to undesired solvent co-intercalation that occurs with graphitic anodes. Here, we show that fluoroethers are the first class of ether solvents to intrinsically support reversible lithium-ion intercalation into graphite without solvent co-intercalation at conventional salt concentrations. In full cells using a graphite anode, they enable 10-fold higher energy densities compared to conventional ethers, and better thermal stability over carbonate electrolytes (operation up to 60 °C) by producing a robust solvent-derived solid electrolyte interphase (SEI). As single-solvent–single-salt electrolytes, they remarkably outperform carbonate electrolytes with fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) and vinylene carbonate (VC) additives when cycled with graphite–silicon composite anodes. Our molecular design strategy opens a new class of electrolytes that can enable next generation Li-ion batteries with higher energy density and a wider working temperature window.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...