High performance Li-, Na-, and K-ion storage in electrically conducting coordination polymers†
Abstract
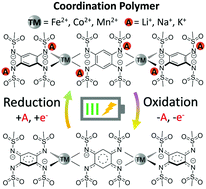
Coordination polymers (CPs) made of redox-active organic moieties and metal ions emerge as an important class of electroactive materials for battery applications. However, the design and synthesis of high voltage alkali-cation reservoir anionic CPs remains challenging, hindering their practical applications. Herein, we report a family of electrically conducting alkali-cation reservoir CPs with the general formula of A2-TM-PTtSA (wherein A = Li+, Na+, or K+; TM = Fe2+, Co2+, or Mn2+; and PTtSA = benzene-1,2,4,5-tetra-methylsulfonamide). The incorporation of transition metal centers not only enables intrinsic high electrical conductivity, but also shows an impressive redox potential increase of as high as 1 V as compared to A4-PTtSA analogues, resulting in a class of organometallic cathode materials with a high average redox potential of 2.95–3.25 V for Li-, Na- and K-ion batteries. A detailed structure – composition – physicochemical properties – performance correlation study is provided relying on experimental and computational analysis. The best performing candidate shows excellent rate capability (86% of the nominal capacity retained at 10C rate), remarkable cycling stability (96.5% after 1000 cycles), outstanding tolerance to low carbon content (5 wt%), high mass loading (50 mg cm−2), and extreme utilisation conditions of low earth orbit space environment tests. The significance of the disclosed alkali-ion reservoir cathodes is further emphasized by utilizing conventional Li-host graphite anode for full cell assembly, attaining a record voltage of 3 V in an organic cathode Li-ion proof-of-concept cell.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...