Exploiting anion and cation redox chemistry in lithium-rich perovskite oxalate: a novel next-generation Li/Na-ion battery electrode†
Abstract
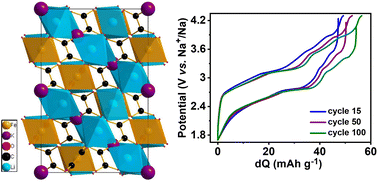
The fundamental understanding of electrochemical reaction kinetics for lithium/sodium-ion batteries (LIBs & NIBs) is a significant criterion for advancing new-generation electrode materials. Herein, we demonstrate a novel lithium-rich perovskite oxalate KLi3Fe(C2O4)3 (KLFC) cathode with the combination of cation and anion redox delivering discharge capacities of 86 and 99 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles for a LIB and NIB, respectively, with good cyclability. Experimental Raman spectroscopy analysis combined with DFT calculations of charged/discharged samples illustrate the oxalate anion redox activity. Further, first-principles calculations of the partial density of states and Bader charges analysis have also characterised the redox behaviour and charge transfer during the potassium extraction processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...