Exploring the synergistic effect of alloying toward hydrogen evolution reaction: a case study of Ni3M (M = Ti, Ge and Sn) series†
Abstract
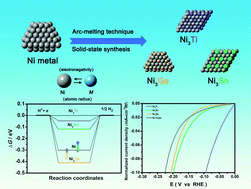
In this work, we have demonstrated that one can control the intrinsic activity of Ni metal toward the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) by simply alloying Ni with different elements (i.e. Ti, Ge or Sn). The HER activities of Ni3M (M = Ti, Ge and Sn) series and Ni metal follow the order of Ni3Ti (η10 = 68 mV) > Ni3Sn (η10 = 122 mV) > Ni3Ge (η10 = 161 mV) > Ni (η10 = 273 mV). After normalizing their HER performances based on the roughness factor (RF), it was realized that Ni3Ti and Ni3Sn both exhibit higher intrinsic HER activities than that of Ni metal while Ni3Ge displays the worst HER performance. This trend was later rationalized by using density functional theory (DFT) calculation, which showed that blending Ni with Ti, Ge or Sn elements will alter the corresponding electronic structure and bonding scheme. Such a change in the bonding scheme (i.e. bonding state or antibonding state) will influence the adsorption energy of the H atom (ΔGHad) on an active site and is the main cause of the synergetic effect that results in the different HER efficiencies of Ni3M (M = Ti, Ge and Sn). Through the present case study, it was recognized that alloying is a simple yet effective strategy to promote the HER activity of an electrocatalyst. With a suitable combination between elements, it helps single metals (e.g. Co or Ni metal) exceed the limits on their intrinsic HER activities and has the potential to replace noble metals (e.g. Pt, Ir and Ru) in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...