An excited state intramolecular proton transfer induced phosphate ion targeted ratiometric fluorescent switch to monitor phosphate ions in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells†
Abstract
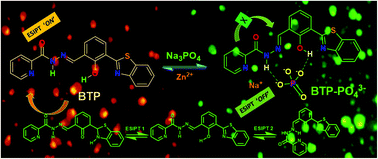
Detection of biological phosphate is very important for environmental and health care applications. In this study, a new ratiometric fluorescent probe (E)-N′-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) picolinohydrazide (BTP) is developed and exhibits a prominent excited-state intramolecular proton-transfer (ESIPT) mechanism. The probe BTP undergoes a unique phosphate induced hydrolytic reaction in mixed aqueous solution which produces a colorimetric change associated with a huge red-shift of ∼130 nm in the UV–visible absorption spectrum. Initially, BTP exhibits a strong fluorescence emission as the ESIPT process is ‘on’ and the tautomeric hydrogen remains flexible and is free to give two tautomeric forms. Eventually, after the addition of PO43−, the two tautomeric forms break and thereby shift the equilibrium towards the ‘enol’ form. The phosphate ion binds with BTP which is associated with a ratiometric change and accounts for an enhancement in the fluorescence intensity with a large blue shift and the limit of detection value of 8.33 × 10−8 M in a mixed aqueous medium. The binding constant (1.92 × 105 M−1) proportionally reflects the stability of the complexation between the binding sites of BTP with the guest PO43− anion. The probable mechanism is supported by the NMR spectroscopy studies. The sensing phenomenon is found to be reversible towards Zn2+ and thus the sensor beautifully mimics the INHIBIT logic gate. Observations have been made in fluorescence imaging studies with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) which indicates that BTP can be employed to successfully monitor the phosphate ion in human PBMCs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Europe


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...