Cytotoxic properties of rhenium(i) tricarbonyl complexes of N-heterocyclic carbene ligands†
Abstract
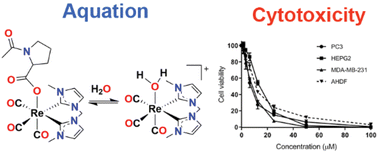
A family of eight rhenium(I) tricarbonyl complexes bearing pyridyl-imidazolylidene or bis-imidazolylidene ligands in combination with a series of N-acetyl amino acids ligands (glycine, isoleucine, and proline) and an acetate have been synthesised and characterised. These complexes are of interest as potential anticancer agents, where the oxygen bound carboxylate ligand can exchange with water giving rise to cytotoxic cationic complexes. The pseudo-first-order aquation rate constants for the complexes were evaluated using 1H NMR time-course experiments and for the complexes of the bis-imidazolylidene ligand the average k1 value was 6.22 × 10−5 s−1 while for the pyridyl-imidazolylidene ligand the aquation rate was slower with the average k1 value being 3.00 × 10−5 s−1. Cytotoxicity studies in three cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231, PC3 and HEPG2) showed that the Re(I) complexes of the bis-imidazolylidene ligand were significantly more toxic than those of the pyridyl-imidazolylidene ligand.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...