ULSA: unified language of synthesis actions for the representation of inorganic synthesis protocols
Abstract
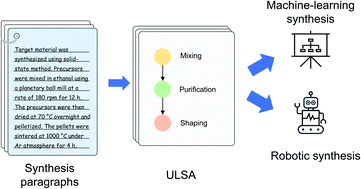
Applying AI power to predict syntheses of novel materials requires high-quality, large-scale datasets. Extraction of synthesis information from scientific publications is still challenging, especially for extracting synthesis actions, because of the lack of a comprehensive labeled dataset using a solid, robust, and well-established ontology for describing synthesis procedures. In this work, we propose the first unified language of synthesis actions (ULSA) for describing inorganic synthesis procedures. We created a dataset of 3040 synthesis procedures annotated by domain experts according to the proposed ULSA scheme. To demonstrate the capabilities of ULSA, we built a neural network-based model to map arbitrary inorganic synthesis paragraphs into ULSA and used it to construct synthesis flowcharts for synthesis procedures. Analysis of the flowcharts showed that (a) ULSA covers essential vocabulary used by researchers when describing synthesis procedures and (b) it can capture important features of synthesis protocols. The present work focuses on the synthesis protocols for solid-state, sol–gel, and solution-based inorganic synthesis, but the language could be extended in the future to include other synthesis methods. This work is an important step towards creating a synthesis ontology and a solid foundation for autonomous robotic synthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...