Role of iron contaminants in the pathway of ultra-stable Y zeolite degradation†
Abstract
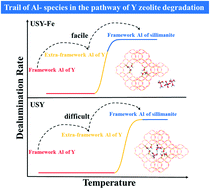
Fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) plays a vital industrial role globally. The factors influencing the stability of zeolite Y in the presence of iron contaminants remain one of the most important topics related to catalyst design. By using a range of spectroscopic techniques, including XRD, 27Al MAS NMR, STEM, 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy and synchrotron XAS, the role of iron contaminants in the degradation and crystal transformation of USY zeolite was investigated in this study. The results of XRD and 27Al MAS NMR show that, for the USY zeolite, the dramatic collapse of its crystal structure occurs above 1000 °C, which is mainly due to the removal of the framework aluminum and its transformation to non-framework aluminum upon thermal heating. In contrast, for the iron-contaminated USY zeolite, the framework aluminum is rapidly removed at 900 °C, and the non-framework aluminum formed subsequently migrates to the surroundings of the iron atom. At 1000 °C, the non-framework aluminum transforms into sillimanite, a component containing iron and silicon with a low specific surface area and non-catalytic activity. The results of STEM mapping show that the introduction of iron promotes the migration of non-framework aluminum and the formation of large clusters around iron. The XANES and MS analyses suggest that the Fe in the USY zeolites is mainly in the form of Fe(III) with an isomer shift of about 0.30(5) mm s−1, and that the valence state of iron increases with increasing calcination temperature. EXAFS results confirm the substitution of Fe atoms for Al in the sillimanite frame and the newly formed Fe–Si has an Fe–Si bond length of 3.3 Å. These results should shed light on the iron poisoning issues in FCC units.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...